GSM stands for Global System for Mobile Communications. It is a standard set developed by the European Telecommunications Standards Institute (ETSI) to describe technologies for second generation (2G) digital cellular networks.

GSM Security Feature
Security in GSM consists of the following aspects: subscriber identity authentication, subscriber identity confidentiality, and user and signaling data confidentiality.
- Subscriber identity authentication
It uses a challenge response protocol for which the fixed network authenticates the identity of mobile subscribers. - Subscriber identity confidentiality
Subscriber identity confidentiality means that the operator tries to protect the user’s telephone number from unauthorized tapping, such that information is disclosed only to those who are authorized to view it. - User and signaling data confidentiality
Signalling and data channels are protected over the radio path. Privacy of user-generated data is provided for both voice and non-voice transferred over the radio path on traffic channels. Privacy for user data transferred in packet mode over the radio path on dedicated signaling channels is also provided. Encrypted voice and data communication between the MS (Mobile Station) and the network is achieved through the ciphering algorithm A5.
GSM Threats and Solution
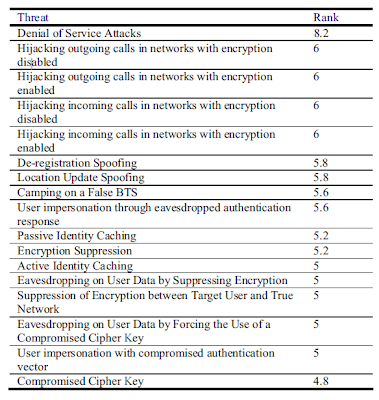
The table above summarizes the threats and their ranks. It is easily observable that the most serious threat is the denial of service attack.
So what are the solution to these problems?
- Use secure algorithms for A3/A8 implementations
This can thwart the dangerous SIMcard cloning attack - Use secure ciphering algorithms
Operators can use newer and more secure algorithms such as A5/3 provided that such improvements are allowed by the GSM consortium. - Securing the backbone traffic
Encrypting the backbone traffic between the network components can prevent the attacker to eavesdrop or modify the transmitted data. - End-to-end security
The best, easiest, and most profitable solution is to deploy the end-to-end security or security at the application layer.
Reference
Academia.edu
VTT Research Notes
Hi zhou ran, I think your post is quite detailed and understandable. Under the table, you say that denial of service attack is the most serious threat since it is ranked the highest. Maybe you can write out a short paragraph to elaborate more on it?
ReplyDeleteHi Zhuo Ran!! I think yours have a good elaboration. and I will add the threats of the GSM.
ReplyDeleteEavesdropping. This is the capability that the intruder eavesdrops signalling and data connections associated with other users. The required equipment is a modified MS.
• Impersonation of a user. This is the capability whereby the intruder sends signalling and/or user data to the network, in an attempt to make the network believe they originate from the target user. The required equipment is again a modified MS.